
The fullonica (fullery) was built in the early 2nd century AD by converting a house of an earlier period. It consisted of a huge room with a roof supported by pillars, hosting four large basins connected to one another and lined with cocciopesto, a coating that served to...

The domus (house) was installed in the second half of the 3rd century AD on the ground floor of an earlier apartment building (insula) of the Hadrianic period (ca. AD 130). Both the original entrance (A) with brick half-columns and the internal layout, arranged around a corridor...
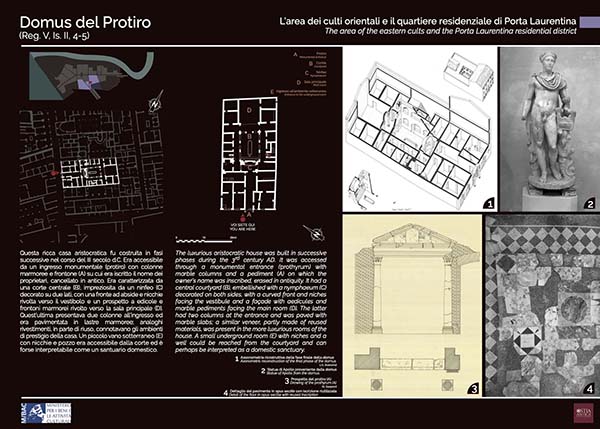
The luxurious aristocratic house was built in successive phases during the 3rd century AD. It was accessed through a monumental entrance (prothyrum) with marble columns and a pediment (A) on which the owner’s name was inscribed, erased in antiquity. It had a central courtyard (B),...

In the early 2nd century AD, the complex consisted of a series of shops with an open space behind them in which a small temple (A) dedicated to an unknown god was built in around AD 200. In the second half of the 3rd century AD, the building became the headquarters of a Neoplatonic...

The aristocratic domusth (house), whose current appearance dates to the 4 century AD, was installed inside a house of the mid-2nd century AD of which it preserved the peristyle in the central courtyard. The entrance was monumentalized with a prothyrum (colonnaded entrance) (A)...

The cult place dedicated to the eastern god Mithras was installed in the second half of the 3rd century AD inside an earlier complex with shops. One of the back rooms of a shop was transformed into a cult space where the podia (side benches) and a small altar were made from reused...
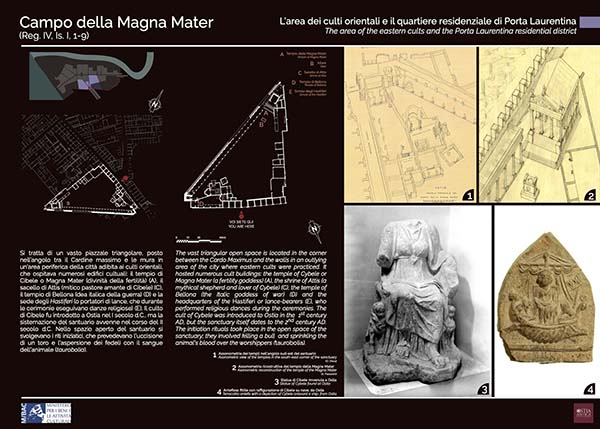
The vast triangular open space is located in the corner between the Cardo Maximus and the walls in an outlying area of the city where eastern cults were practiced. It hosted numerous cult buildings: the temple of Cybele or Magna Mater (a fertility goddess) (A), the shrine of Attis (a mythical...

The gate in the Republican walls, built in around the mid-1st century BC, marks the entrance into the city from the Via Laurentina, an ancient road leading from Laurentum (a town in Lazio south of Rome); the stretch of road inside the city was Ostia’s Cardo Maximus. The gate’s...

The monumental nymphaeum, built in the 4th century AD, takes the form of a single square room, closed and completely covered in marble panels, which provided a backdrop for the jets of water that gushed from a labrum (basin) set inside a central square pool. The side walls of the...

The domus (house) was installed in an earlier residence with a porticoed courtyard and had two main construction phases, the last of which can be dated to the 3rd century AD. The domus is currently accessed through the original service entrance (A), which leads into a porticoed...

The building, used for the production and sale of bread, was built in around AD 120 and was destroyed by a fire in the late 3rd century AD. It had six tabernae (shops) (A) at the front, whilst the inner rooms, floored with road paving stones, served to mill the flour (B) and make the...

The complex, perhaps originally four storeys tall with shops facing onto the street, was built in the Hadrianic period (first half of the 2nd century AD). It has a central porticoed courtyard (C) and over time underwent significant alterations to both the internal walls and the floors. The...

The building, used as an inn with a wine bar, was installed in the 3rd century AD inside a complex of the Hadrianic period (first half of the 2nd century AD). It opened onto the street with three entrances, provided with seats and covered by balconies resting on brackets. The interior was...

The building, known already from the 15th century as the Casone del Sale (salt warehouse), was linked to the exploitation of Ostia’s Papal salt pans. Initially, it took the form of a structure with a pitched roof, with a hollow space beneath the floor to protect against damp. After a...

This marble corbel is one of two that originally decorated the shrine in Ostia’s Synagogue holding the ark in which the scrolls of the Law (Torah) were kept; the construction of this shrine is mentioned by a Greek inscription commemorating an individual who paid for a container to...

The complex had a commercial function and was built at the same time as the nearby Insula dei Dipinti in the Hadrianic period (AD 117-138). It had a row of shops opening onto the street with a vast space behind them: in the early 3rd century AD the latter was transformed into a storage area...

The insula (apartment building) occupies part of the residential area known as the Caseggiato dei Dipinti of the Hadrianic period (AD 117-138), with houses opening onto the street and a large communal courtyard behind (A). The layout has a central corridor (B) and a small...

The castrum is the oldest part of the city of Ostia to be documented archaeologically; it dates to the 4th century BC. It is a fortified settlement surrounded by walls in tufa blocks with four gates, located at the ends of the main streets (the Cardo and Decumanus). Other streets at...